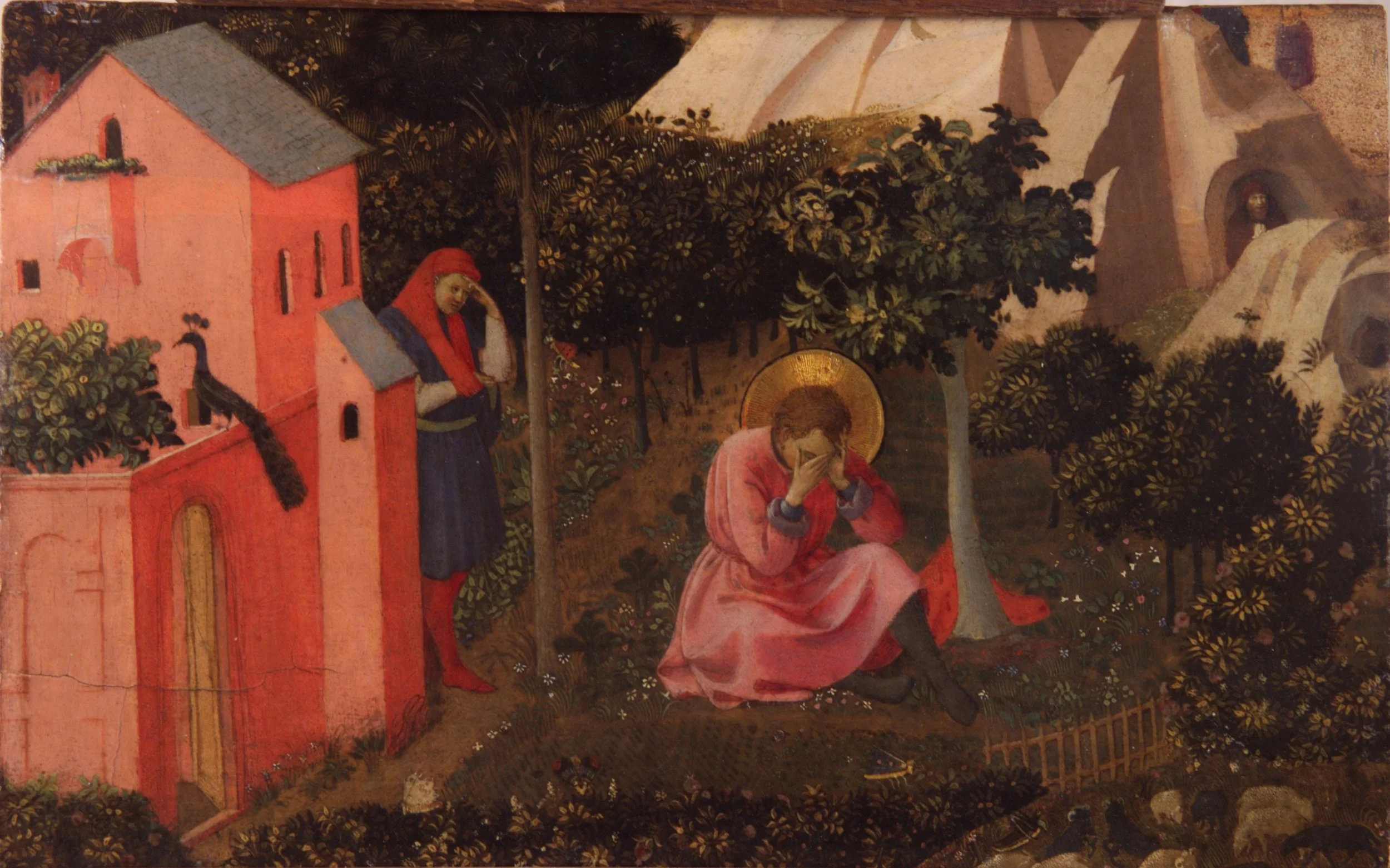
This article argues that Augustine’s identity in the Confessions is not fixed or purely inward, but is continually reshaped through relationships marked by friendship, love, and death. By examining the deaths of close companions—alongside enduring friendships with figures such as Alypius, Nebridius, and Monica—it shows how grief destabilizes Augustine’s sense of self and ultimately redirects his love toward God as its proper end. The study contends that friendship functions as a crucial mediator between self-knowledge and divine knowledge, revealing identity as relational, mutable, and ordered through rightly directed love.
Read MoreBy Victor Zou
Beowulf is a classic and ancient Anglo-Saxon hero’s tale. The various monstrosities he faces define his story and character. His defeat of Grendel, his atrocious mother, and the dragon all reflect his prowess and courage as a heroic champion. But these victories also encourage the growth of ill-fated attitudes. As J. Leyerle describes, he is a hero that “follows a code that exalts indomitable will and valor in the individual.”[1] In fact, the more Beowulf grows as a heroic warrior the more independent and prideful he becomes. And yet, in the midst of this he is pushed towards taking on the role of a king, which is a role he is woefully unfit to take. To lead a people-group requires a willingness to cooperate and a humility that a Beowulfian hero is simply disinclined to have. This disconnect between both ideals is the crux of Beowulf’s journey. While Beowulf assumes both positions, there is a clear distinction between the characteristics of a successful hero and a successful king. Thus, the tale acts as a critique of a heroic culture that values pride and independence by showing the dangerous tendencies that this encourages, and what can happen when a hero is given power and responsibility.
Read More
By Rosalind Fursland
Mina Loy is primarily known as an early modernist poet, although she was also an admired creator in other spheres. One of Loy’s most recognisable and insightful remarks in her essay “Modern Poetry” is that “Poetry is prose bewitched, a music made of visual thoughts, the sound of an idea” (Loy 157)
Read MoreBy Quinn Gilman-Forlini
The Book of Repulsive Women is a collection of eight poems and five drawings by Djuna Barnes first published in 1915. Despite the fact that this was Barnes’ first publication of what she considered to be her “serious” work, she later hated the book and wished to repress the fact that she had written it at all.
Read MoreBy Joseph Witkin
Paul Valéry’s “Philosophy of the Dance” may have ekphrastic potential, but before suggesting that the author’s words give voice to the dance, a strong association between word and the dancer’s image must be formed.
Read More